Table of Contents
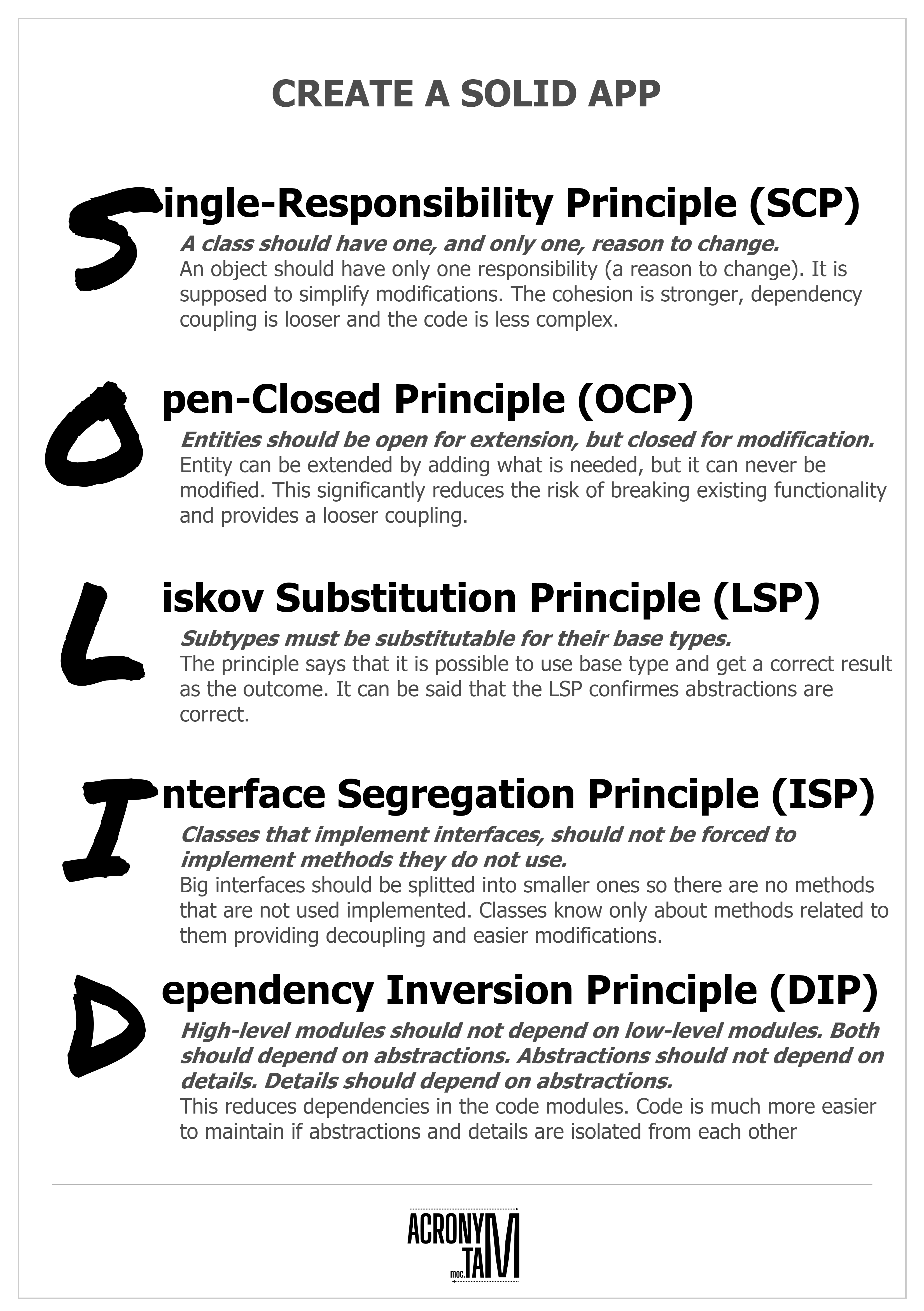
1. S - Single Responsibility Principle (Nguyên tắc trách nhiệm duy nhất)
Định nghĩa: Một class chỉ nên có một lý do để thay đổi, tức là một class chỉ nên có một trách nhiệm hoặc chức năng duy nhất.
Ví dụ:
// Sai cách: Lớp User có quá nhiều trách nhiệm class User { public function getName() { // logic lấy tên } public function saveToDatabase() { // logic lưu trữ thông tin vào cơ sở dữ liệu } } // Đúng cách: Tách biệt các trách nhiệm class User { public function getName() { // logic lấy tên } } class UserRepository { public function save(User $user) { // logic lưu trữ thông tin vào cơ sở dữ liệu } }
2. O - Open/Closed Principle (Nguyên tắc mở/đóng)
Định nghĩa: Một class nên được mở để mở rộng nhưng đóng để chỉnh sửa.
Ví dụ:
// Sai cách: Thay đổi trực tiếp vào class class Rectangle { public function area($width, $height) { return $width * $height; } } class Circle { public function area($radius) { return pi() * $radius * $radius; } } class AreaCalculator { public function calculate($shapes) { $area = 0; foreach ($shapes as $shape) { if ($shape instanceof Rectangle) { $area += $shape->area($shape->width, $shape->height); } else if ($shape instanceof Circle) { $area += $shape->area($shape->radius); } } return $area; } } // Đúng cách: Sử dụng interface để mở rộng chức năng interface Shape { public function area(); } class Rectangle implements Shape { private $width; private $height; public function __construct($width, $height) { $this->width = $width; $this->height = $height; } public function area() { return $this->width * $this->height; } } class Circle implements Shape { private $radius; public function __construct($radius) { $this->radius = $radius; } public function area() { return pi() * $this->radius * $this->radius; } } class AreaCalculator { public function calculate($shapes) { $area = 0; foreach ($shapes as $shape) { $area += $shape->area(); } return $area; } }
3. L - Liskov Substitution Principle (Nguyên tắc thay thế của Liskov)
Định nghĩa: Các đối tượng của lớp con nên có thể thay thế các đối tượng của lớp cha mà không làm thay đổi tính đúng đắn của chương trình.
Ví dụ:
// Sai cách: Lớp con không hoàn toàn tuân thủ hành vi của lớp cha class Bird { public function fly() { return "Flying"; } } class Penguin extends Bird { public function fly() { throw new Exception("Penguins can't fly"); } } // Đúng cách: Tạo các lớp con tuân thủ hành vi của lớp cha hoặc tạo một hierarchy khác class Bird { public function move() { return "Moving"; } } class FlyingBird extends Bird { public function fly() { return "Flying"; } } class Penguin extends Bird { public function swim() { return "Swimming"; } }
4. I - Interface Segregation Principle (Nguyên tắc phân chia interface)
Định nghĩa: Các client không nên bị buộc phải phụ thuộc vào các interface mà họ không sử dụng.
Ví dụ:
// Sai cách: Interface quá lớn chứa nhiều phương thức không liên quan interface WorkerInterface { public function work(); public function eat(); } class HumanWorker implements WorkerInterface { public function work() { // logic làm việc } public function eat() { // logic ăn uống } } class RobotWorker implements WorkerInterface { public function work() { // logic làm việc } public function eat() { // Robots không cần ăn, nhưng vẫn phải implement phương thức này } } // Đúng cách: Chia nhỏ interface interface WorkableInterface { public function work(); } interface EatableInterface { public function eat(); } class HumanWorker implements WorkableInterface, EatableInterface { public function work() { // logic làm việc } public function eat() { // logic ăn uống } } class RobotWorker implements WorkableInterface { public function work() { // logic làm việc } }
5. D - Dependency Inversion Principle (Nguyên tắc đảo ngược sự phụ thuộc)
Định nghĩa: Các module cấp cao không nên phụ thuộc vào các module cấp thấp; cả hai nên phụ thuộc vào abstraction.
Ví dụ:
// Sai cách: Module cấp cao phụ thuộc trực tiếp vào module cấp thấp class MySQLConnection { public function connect() { // logic kết nối MySQL } } class PasswordReminder { private $dbConnection; public function __construct(MySQLConnection $dbConnection) { $this->dbConnection = $dbConnection; } } // Đúng cách: Sử dụng abstraction để giảm sự phụ thuộc interface DBConnectionInterface { public function connect(); } class MySQLConnection implements DBConnectionInterface { public function connect() { // logic kết nối MySQL } } class SQLiteConnection implements DBConnectionInterface { public function connect() { // logic kết nối SQLite } } class PasswordReminder { private $dbConnection; public function __construct(DBConnectionInterface $dbConnection) { $this->dbConnection = $dbConnection; } }
Tham khảo: